Ensuring legal compliance is a critical yet complex responsibility for any business.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of legal compliance fundamentals, explaining what compliance entails and why it matters, as well as outlining strategies and best practices for developing a robust compliance program.
You'll learn key compliance areas to prioritize, like adhering to workplace regulations and protecting sensitive data, along with practical guidance on compliance audits, training, and more.Whether you're looking to build a compliance program from scratch or optimize an existing one, this guide has actionable insights to help strengthen legal compliance in your company.
Introduction to Legal Compliance in Company Management
Legal compliance refers to a company's adherence to laws and regulations relevant to their industry and business operations. Maintaining compliance is crucial for companies to avoid penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage. This section provides an overview of legal compliance, outlines its importance, and previews some key compliance requirements for companies.
Understanding Legal Compliance Meaning
Legal compliance means that a company follows all applicable federal, state, and local laws and regulations. This includes requirements related to:
- Licenses, permits, and certifications
- Workplace health and safety
- Marketing and advertising
- Privacy and data protection
- Industry-specific regulations
Adhering to these laws ensures companies operate ethically and fulfill all legal obligations. It also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
The Importance of Legal Compliance
Legal compliance is essential for companies for several reasons:
- Avoids penalties and legal action: Violating laws can result in fines, business interruptions, and lawsuits. Effective compliance protects companies.
- Upholds business integrity: Legal and ethical conduct improves public image and instills confidence in the brand.
- Enhances decision-making: Understanding legal obligations informs business decisions and minimizes risk.
- Meets stakeholder expectations: Shareholders, customers, and partners expect legal compliance from companies they engage with.
Overview of Legal Compliance Requirements
Key legal compliance areas companies must address include:
- Business licenses, permits, and annual filings
- Workplace regulations
- Marketing and advertising laws
- Privacy laws and data security protocols
- Industry-specific regulations
Later sections will explore these requirements and compliance best practices in greater detail. Adopting compliance procedures is essential for risk management.
Why is legal compliance important in business?
Legal compliance is crucial for companies to operate ethically, avoid penalties, and build trust with customers. By following regulations, businesses demonstrate accountability and responsibility.
Here are key reasons legal compliance matters:
- Avoids lawsuits & fines: Violating laws can lead to expensive lawsuits or fines from agencies like the FTC, EPA, OSHA which hurt profits. Having compliance programs helps prevent issues.
- Protects reputation: When scandals happen from non-compliance like privacy breaches, it damages public trust. Legal compliance maintains credibility.
- Meets industry standards: Companies that ignore compliance appear unsafe and poorly managed to partners. Meeting requirements shows capabilities.
- Supports decisions: Keeping legally compliant records from compliance audits helps leadership make sound choices protecting the company.
- Attracts investment: Investors see legal compliance as a sign of good governance and ethical operation worth funding. This enables growth.
While staying compliant takes resources, it saves money over the long run. Plus, legal compliance supports stable business operations and strategy. Reviewing current regulations and having systems to meet rules is essential.
What is corporate legal compliance?
Corporate legal compliance refers to a company's adherence to relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies. It is crucial for organizations to have robust compliance programs to avoid legal issues and protect their reputation.
Some key aspects of corporate legal compliance include:
- Business licenses and permits: Ensuring your company has all required licenses and permits to legally operate. This varies by industry, location, business structure, etc.
- Annual filings and reports: Properly submitting annual reports, tax documents, and other legally required filings. Missing deadlines can lead to penalties.
- Registered agent: Appointing a registered agent to receive official communications and legal notices on behalf of your company.
- Workplace regulations: Abiding by laws related to hiring, employee rights, workplace safety, accessibility, etc. Violations risk lawsuits.
- Marketing and advertising: Following regulations around advertising claims, disclosures, email marketing, telemarketing, etc. to avoid consumer protection issues.
- Data protection: Implementing processes to securely collect, store, use and destroy customer data according to privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA to avoid data breaches.
Having clear compliance policies and regular audits helps companies stay current on evolving legal obligations. It enables them to effectively navigate change instead of reacting to issues. Ultimately, thoughtful compliance protects the business and enables smart decision making.
What is compliance in the company?
Compliance refers to a company's adherence to laws, regulations, industry standards, and ethical codes that apply to its business. Maintaining compliance is crucial for companies to operate legally and avoid penalties.
Some key aspects of legal and regulatory compliance that companies must consider include:
- Business licenses and permits: Companies must obtain all necessary licenses, permits, and certificates required to operate in their jurisdiction. These vary by location, industry, and business activity.
- Tax compliance: Companies must comply with federal, state, and local tax laws by registering for tax IDs, filing returns, and remitting payments on time.
- Employment laws: Laws related to hiring, compensation, workplace safety, discrimination, and more must be followed to avoid lawsuits.
- Industry regulations: Industries like finance, healthcare, transportation, etc. have specific regulatory bodies that issue mandatory rules to follow.
- Data protection laws: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA govern how personal data can be collected, processed, shared and secured.
- Accessibility standards: Websites, software and facilities may need accommodations to comply with disability access laws like the ADA.
- Reporting requirements: Most business structures have annual filing and reporting requirements to transparency authorities.
Maintaining legal and regulatory compliance protects companies from lawsuits, penalties, shutdowns and reputational damage. It also builds customer and stakeholder trust.
Dedicated compliance professionals and audits help companies stay current on evolving regulations. Compliance training also keeps staff aware of mandatory policies and required procedures. Overall, legal compliance enables businesses to sustainably operate and scale.
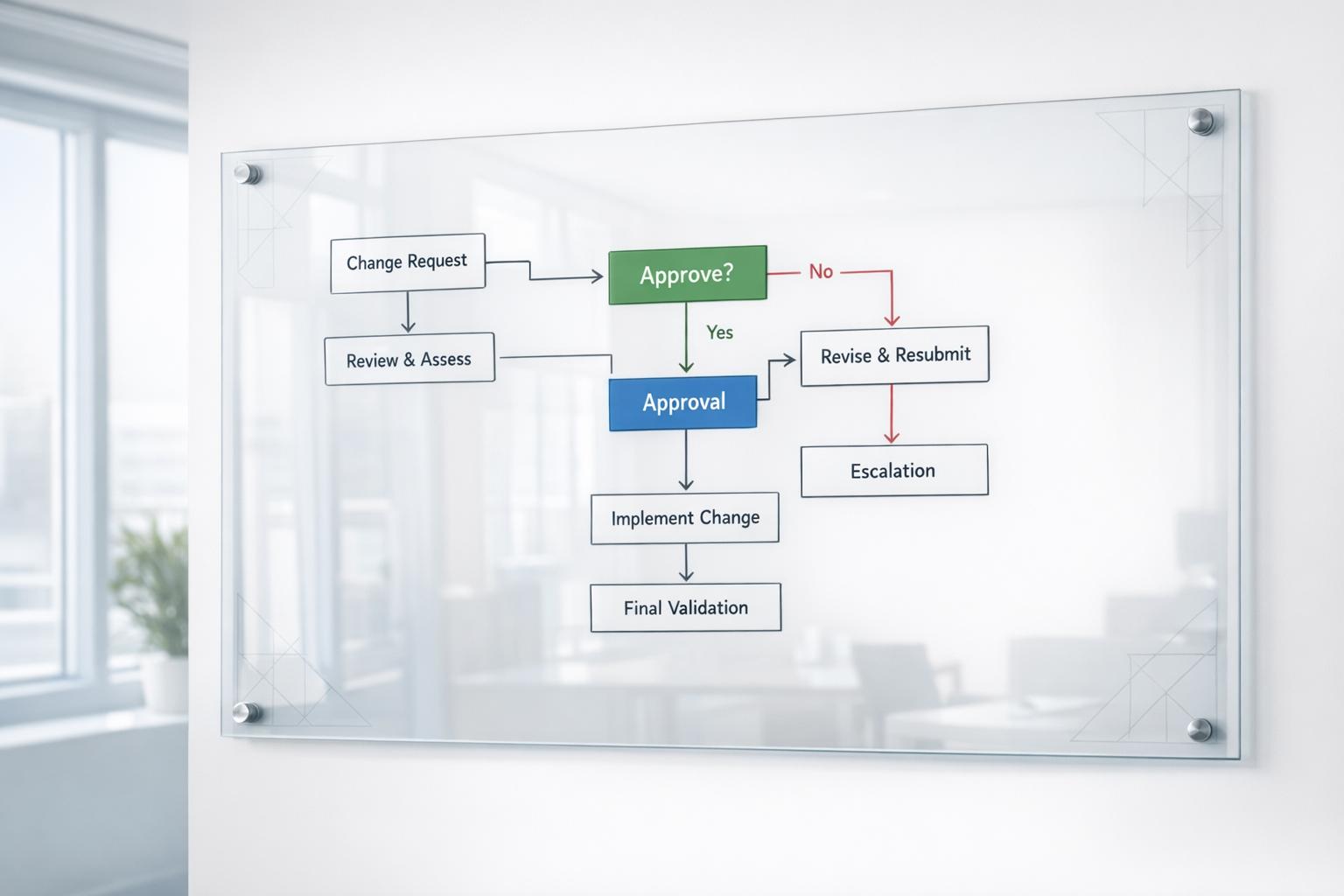
How do you maintain legal compliance?
To stay legally compliant as a company, it is important to develop a compliance program that includes ongoing audits and reviews. Here are some key steps:
Understand compliance requirements
The first step is to understand the legal and regulatory compliance requirements that apply to your company based on factors like:
- Business structure (LLC, C-Corp, S-Corp, etc.)
- Industry (healthcare, financial services, retail, etc.)
- Locations of operation
- Data collection and storage practices
Major compliance categories can include:
- Licenses and permits
- Taxes and annual filings
- Workplace regulations
- Data privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA)
- Industry-specific regulations (HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOX)
Conduct risk assessments
Conduct regular risk assessments to identify areas of compliance vulnerability. Review business practices against requirements and pinpoint any gaps.
Develop compliance policies
Draft comprehensive policies that align with legal obligations across business units. Clearly document standards procedures for achieving and maintaining compliance.
Assign oversight responsibilities
Appoint compliance officers to develop programs, assign accountability, oversee policy implementation, perform audits, and report to leadership.
Train employees
Educate all employees and stakeholders on compliance policies and their legal responsibilities through training programs. Stress the importance of compliance.
Monitor and audit
Routinely monitor business operations and conduct internal audits to validate that compliance standards are being upheld. Evaluate effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Staying legally compliant takes consistent commitment across an organization. Following structured policies and enabling employee awareness empowers companies to avoid penalties and build trust.
Establishing a Compliant Business Framework
Selecting the Appropriate Business Structure
When starting a business, one of the first decisions owners must make is choosing the appropriate business structure. The most common options include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), S corporation, and C corporation. Each structure has different legal and tax implications that impact the company's compliance requirements. For example, corporations must adhere to more formalities like holding shareholder meetings and issuing stock, while sole proprietors report business income on their personal tax returns. When selecting a business structure, owners should consider liability protection, taxation rules, ownership flexibility, and compliance complexity. An informed decision helps establish a compliant framework from the outset.
Acquiring Business Licenses and Permits
Beyond formal registration, most businesses need licenses and permits to legally operate. The specific requirements vary by industry, location, business activities, and local regulations. Still, some common licenses and permits include a sales tax permit, food handler's permit, liquor license, general business license, home occupation permit, trade/contractor's license, and zoning permit. Failing to acquire the necessary licenses opens businesses to penalties, fees, and potential closure. Therefore, thoroughly researching and complying with licensing ensures smooth operations. Some useful resources for determining licensing requirements include state and local government websites, SBA guidance, legal consultants, and permit expeditors.
Understanding Annual Filing Requirements
Depending on the business structure, companies must complete annual filings to remain legally compliant. For example, corporations must file an annual report and pay fees to stay active and in good standing. The report confirms up-to-date company information like directors, officers, business activities, and registered agents. Partnerships and LLCs also submit annual statements and taxes to renew permits and licenses. Additionally, all businesses must file annual federal, state, and local tax returns. Other common annual filings include 1099 forms for independent contractors, annual minutes for corporations, and renewing licenses, permits, and certifications. Keeping up with filing deadlines prevents penalties and business disruptions.
The Role of a Registered Agent in Compliance
A registered agent, also called a resident agent or statutory agent, is an individual or business entity authorized to receive legal correspondence on behalf of a company. They provide a physical address where important legal and tax documents can be served. Registered agents have a critical compliance role - they forward summons, lawsuits, subpoenas, and notices to the appropriate company leaders so the business can respond appropriately. Appointing a competent registered agent who actively forwards documents is vital for avoiding missing critical legal notifications. Some registered agents also provide compliance advice, reminders about filing deadlines, and address forwarding services. These value-added offerings further strengthen compliance.
Navigating the Corporate Transparency Act
The Corporate Transparency Act, enacted in 2021, aims to combat financial crimes by requiring certain corporations and LLCs to report ownership and control information to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). This increases transparency around shell companies used for money laundering and other illegal activities. Under the law, covered companies must identify and provide personal information on their underlying beneficial owners - individuals with significant control or 25%+ ownership stakes. Companies must also keep ownership information updated by filing reports within 30 days of changes. As regulations and enforcement plans solidify, businesses should prepare to meet disclosure requirements and adapt practices accordingly. Proactive navigation of the Corporate Transparency Act facilitates sustained compliance.
sbb-itb-d1a6c90
Compliance with Workplace Regulations
Companies must comply with various workplace laws and regulations to ensure a lawful and ethical working environment for their employees. Key areas of compliance include:
Adhering to Workplace Poster Laws
Companies are required by law to display certain posters in the workplace that inform employees of their rights and company policies. These posters cover topics such as equal employment, family medical leave, minimum wage, occupational health and safety, and more. Failure to properly display all required posters can result in fines or other penalties.
To comply, companies should:
- Identify all federal, state, and local poster requirements that apply to your business
- Acquire necessary posters from the Department of Labor or other government agencies
- Visibly display posters in areas frequented by employees such as breakrooms
- Replace outdated posters whenever regulations change
- Provide posters in languages spoken by significant portions of workforce
Ensuring Workplace Health and Safety Compliance
Companies must comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and other health and safety regulations to prevent illness, injury, and death in the workplace. This involves:
- Providing adequate protective gear, safety equipment, and training
- Ensuring proper ventilation, temperature, lighting and sanitation
- Implementing safety protocols, emergency plans, inspection procedures
- Keeping records of illnesses, injuries, and exposure to contaminants
- Correcting any hazards or violations discovered
Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, fines, business disruptions, and damage to company reputation.
Compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The ADA prohibits discrimination against those with disabilities and mandates that employers provide reasonable accommodations to allow equal employment opportunities. Compliance requires:
- Making hiring, firing, and promotion decisions without regard to disability
- Making facilities, information, and processes accessible to those with disabilities
- Providing assistive equipment, schedule changes, or work adjustments for disabled employees unless posing undue hardship
ADA violations can lead to government investigations, lawsuits, and requirement to pay employee damages.
Preventing Workplace Discrimination and Harassment
Companies must foster a professional environment free from unlawful discrimination and harassment. This includes:
- Establishing clear anti-discrimination and anti-harassment policies
- Providing regular employee training on recognizing and preventing inappropriate workplace conduct
- Implementing reporting procedures and promptly investigating claims
- Taking immediate and appropriate action upon discovering misconduct
Failure to sufficiently address workplace discrimination and harassment can greatly impact employee morale, productivity, and retention as well as expose the company to lawsuits.
Data Protection and Privacy Compliance
This section addresses the critical need for companies to ensure data protection and follow mandatory regulatory compliance practices to safeguard sensitive information.
Compliance with PCI DSS for Payment Security
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of requirements for companies that process, store or transmit payment card data, such as credit cards. Adhering to PCI DSS is mandatory for ensuring secure transactions and protecting sensitive cardholder information.
Key aspects of PCI DSS compliance include:
- Building and maintaining a secure network with firewalls
- Protecting cardholder data through encryption
- Maintaining a vulnerability management program
- Implementing access controls with need-to-know access
- Regularly monitoring and testing networks
Violations can lead to fines, damaged reputation, and loss of customers. By implementing proper controls and validation checks, companies can avoid non-compliance issues.
Adhering to HIPAA for Patient Privacy
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets standards for handling protected health information (PHI). Companies dealing with patient medical records must have safeguards in place to ensure privacy.
Core aspects of HIPAA compliance are:
- Appointing a privacy officer responsible for compliance
- Conducting risk analysis and implementing safeguards
- Using encryption for storing and transmitting PHI
- Having breach notification procedures
- Providing HIPAA training to employees
Failing to meet requirements can incur penalties. Proactive planning for HIPAA allows healthcare providers to avoid violations.
Meeting GDPR Requirements for EU Data
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) regulates data protection and privacy for EU citizens. Companies handling personal data of EU data subjects must comply with GDPR.
Key GDPR compliance considerations are:
- Documenting lawful basis for data processing
- Handling subject rights requests within deadline
- Anonymizing data where possible
- Reporting breaches within 72 hours
- Confirming compliance through audit
Non-compliance can lead to fines of €20 million or 4% of global revenue. Thus, implementing GDPR controls is vital.
Understanding CCPA and State-Specific Privacy Laws
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives California residents rights over their personal data. Companies serving California must meet its requirements. Other states also have their own privacy laws emerging.
Aspects to handle for state law compliance:
- Providing transparency about data collection
- Allowing consumers to opt out of data sales
- Facilitating requests for data deletion
- Training staff on compliance protocols
- Staying updated on new state regulations
Keeping current with changing state laws allows companies to avoid lawsuits or penalties.
Implementing FISMA Compliance for Federal Data
The Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) mandates security over federal information systems. Companies managing federal data must adhere to NIST guidelines under FISMA.
Key aspects include:
- Categorizing data per impact level
- Following the Risk Management Framework security lifecycle
- Reporting on metrics to federal agencies
- Conducting annual audits for control gaps
- Ensuring only authorized access and proper identity verification
Violating FISMA can lead to loss of federal contracts or lawsuits. Thus compliance is essential.
Developing a Robust Compliance Program
Creating a Legal Compliance Checklist
To ensure full legal compliance, companies should develop a comprehensive checklist covering key areas of business regulation. This includes confirming proper business licenses and permits are in place, workplace safety and non-discrimination laws are followed, and mandatory filings like annual reports are completed.
A compliance checklist should include:
- Business structure and annual filing requirements
- Licenses, permits, or certificates
- Workplace poster laws
- Marketing and advertising regulations
- Privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA
- Industry-specific regulations
Checking off each requirement helps systematically ensure legal obligations are met. The checklist should be updated regularly as regulations change.
Developing Written Compliance Policies and Procedures
Documenting formal compliance policies and procedures ensures consistent adherence to legal standards across the organization. Key steps include:
- Researching all applicable laws and regulations
- Defining roles and responsibilities around compliance
- Outlining specific processes for achieving and maintaining compliance
- Providing guidelines for detecting and reporting violations
Written policies serve as the foundation for compliance training and enable smooth auditing processes. They should be precise, comprehensive, and reflect the company's commitment to integrity.
Conducting Compliance Training and Education
Effective compliance requires properly educating all employees. Training should cover:
- Company policies and legal obligations
- Real-world examples of compliance issues
- How to spot and report violations
- Consequences of non-compliance
This knowledge empowers staff at all levels to uphold standards. Training should be regularly refreshed as policies evolve. Competency validation through testing builds accountability.
Implementing Internal Compliance Monitoring and Audits
Proactive internal auditing identifies control gaps before problems arise. Key aspects include:
- Developing audit schedules and risk-based plans
- Creating processes for detecting violations
- Conducting interviews, inspections, and testing
- Tracking corrective actions for deficiencies
Monitoring employee awareness and validating policy effectiveness allows companies to strengthen compliance programs over time.
Facilitating External Compliance Audits
While internal assessments are crucial, third-party audits provide unbiased evaluation of how fully policies satisfy legal obligations. They:
- Gauge program effectiveness from an outside lens
- Note areas for improvement missed internally
- Offer credibility to customers and regulators
Together, robust internal monitoring and periodic external audits help companies maintain continuous compliance.
Effective Decision Making in Compliance
Compliance should be an integral part of business decisions to mitigate risks. By considering legal requirements early in the process, companies can make informed choices that align with regulations.
Strategies for Compliance-Oriented Decision Making
- Conduct compliance impact assessments for major initiatives. Analyze how decisions affect legal obligations.
- Maintain an up-to-date compliance calendar listing critical deadlines. Consult regularly when making decisions.
- Develop robust compliance training programs. Educated staff are better equipped to spot issues.
- Document decision rationale citing compliance factors. Create an audit trail showing informed choices.
Maintaining a Records Retention Schedule
A records retention schedule outlines the duration various documents must be preserved to meet legal duties. With clear policies, companies can efficiently manage data and retrieval for audits. Key practices include:
- Classifying records by type and retention period.
- Specifying data formats, storage locations and backup systems.
- Assigning staff responsibility for schedule upkeep and training.
- Regularly reviewing schedules to add new record categories.
Handling Legal Compliance Issues
When compliance problems occur, quick and strategic action is required:
- Notify leadership and assemble a response team including legal counsel.
- Halt related business activities that may worsen issues.
- Thoroughly investigate root causes and impacted areas.
- Create a mitigation plan addressing people, processes and systems.
- Document all investigation and remediation steps as evidence.
Analyze incidents to prevent recurrence and incorporate findings into updated training.
Learning from Compliance Breaches
Studying past compliance failures, though difficult, presents opportunity to bolster defenses:
- Perform an objective post-mortem review of contributing factors.
- Identify potential blindspots in policies, controls or staff skills.
- Strengthen risk assessments using insights from problems.
- Establish metrics and testing to monitor high-risk domains.
Revisiting missteps demonstrates commitment to continuous compliance improvement.
Navigating Change and Ensuring Continuous Compliance
Companies must stay ahead of evolving legal and regulatory frameworks to avoid noncompliance issues. By taking a proactive approach, businesses can adapt their compliance strategies as changes arise.
Adapting to Legal and Regulatory Updates
It is critical that companies monitor legal and regulatory changes relevant to their operations. Assigning responsibility to compliance teams to track updates across jurisdictions helps ensure awareness of new requirements. When significant changes occur, such as major data privacy reforms, cross-functional working groups may examine implications and develop action plans. Prioritizing agility, companies can roll out updated policies, procedures, and training to reflect new laws in a timely manner.
Using Risk Management Framework (RMF) in Compliance
A risk management framework (RMF) provides a structured process for assessing and managing compliance risks. Key steps may include:
- Identifying threats related to noncompliance and vulnerabilities in existing safeguards
- Analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of risks materializing
- Evaluating mitigation options such as enhanced controls
- Selecting a treatment plan to lower risk to acceptable levels
- Continuous monitoring through audits and reviews
Updating the RMF as new regulations emerge enables data-driven decision making to prioritize compliance efforts.
Ensuring Audit Preparedness
While the possibility of an audit can seem daunting, simple preparations enable companies to host assessments smoothly. Maintaining organized records and documentation of compliance activities means evidence is readily available if auditors call. Conducting self-audits periodically identifies any gaps to shore up. Education for staff handling sensitive data ensures they understand protocols. By proactively managing compliance programs, teams feel equipped to demonstrate adherence to requirements without disruption.
Implementing Technology for Compliance Management
Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions enable automation for streamlined compliance. Features like policy and risk management, data loss prevention, audit trail tracking, and reporting analytics enhance oversight. As regulations change, RegTech platforms can be updated to monitor new requirements. Cloud delivery also allows for rapid deployment of the latest compliance capabilities. The right tools make it easier for companies to navigate evolving legal landscapes.
Conclusion: Legal Compliance as a Strategic Advantage
Reaffirming the Importance of Legal Compliance
Legal compliance is critical for companies to operate ethically and avoid legal penalties. By following regulations around data protection, workplace safety, marketing laws, and more, companies build trust with customers and authorities. Neglecting compliance can damage a company's reputation and bottom line through lawsuits, fines, and lost business.
Best Practices for Sustained Legal Compliance
To sustain long-term legal compliance, companies should:
- Conduct regular compliance audits and risk assessments
- Create a compliance calendar detailing deadlines
- Designate a compliance officer role
- Establish mandatory compliance training for all employees
- Develop whistleblower and ethics reporting procedures
- Continuously monitor new regulations
Following these best practices builds a culture focused on legal and ethical integrity.
Legal Compliance as a Foundation for Trust
Companies that consistently demonstrate legal compliance establish credibility and trustworthiness. By making compliance a strategic priority aligned with business objectives, companies can strengthen relationships with customers, business partners, regulators, and investors. A robust compliance program is the foundation for continued growth and success.